Your AML system just flagged another legitimate customer. Again. While your compliance team scrambles to manually review what turns out to be a perfectly normal transaction, that customer is sitting in digital limbo, watching their onboarding process crawl to a halt.
This scenario plays out thousands of times daily across financial institutions worldwide. False positives aren't just a technical nuisance: they're systematically destroying customer experiences and bleeding operational resources. The numbers tell a stark story: 40% of customers abandon onboarding processes that exceed 10 minutes, and every false positive alert pushes you dangerously close to that threshold.
The True Cost of Alert Fatigue
False positives occur when legitimate transactions or customers trigger AML monitoring systems incorrectly. What seems like a minor technical glitch creates a cascade of business problems that compound rapidly.
Every false positive requires manual investigation. Your compliance team stops productive work to examine what ultimately proves to be innocent activity: a large bank transfer for a home purchase, a payment for rare collectibles, or routine business transactions that happen to match certain patterns. These investigations consume hours of expert time that should focus on genuine threats.
Meanwhile, legitimate customers experience frustration and damaged trust. They're subjected to additional verification steps, longer wait times, and repeated requests for documentation. In competitive markets, these customers simply take their business elsewhere rather than endure invasive screening for routine transactions.
The operational burden extends beyond immediate costs. High false positive rates trigger regulatory scrutiny, as they indicate potential inefficiencies in your AML program. Regulators expect institutions to demonstrate that their systems accurately identify genuine risks without creating excessive operational noise.
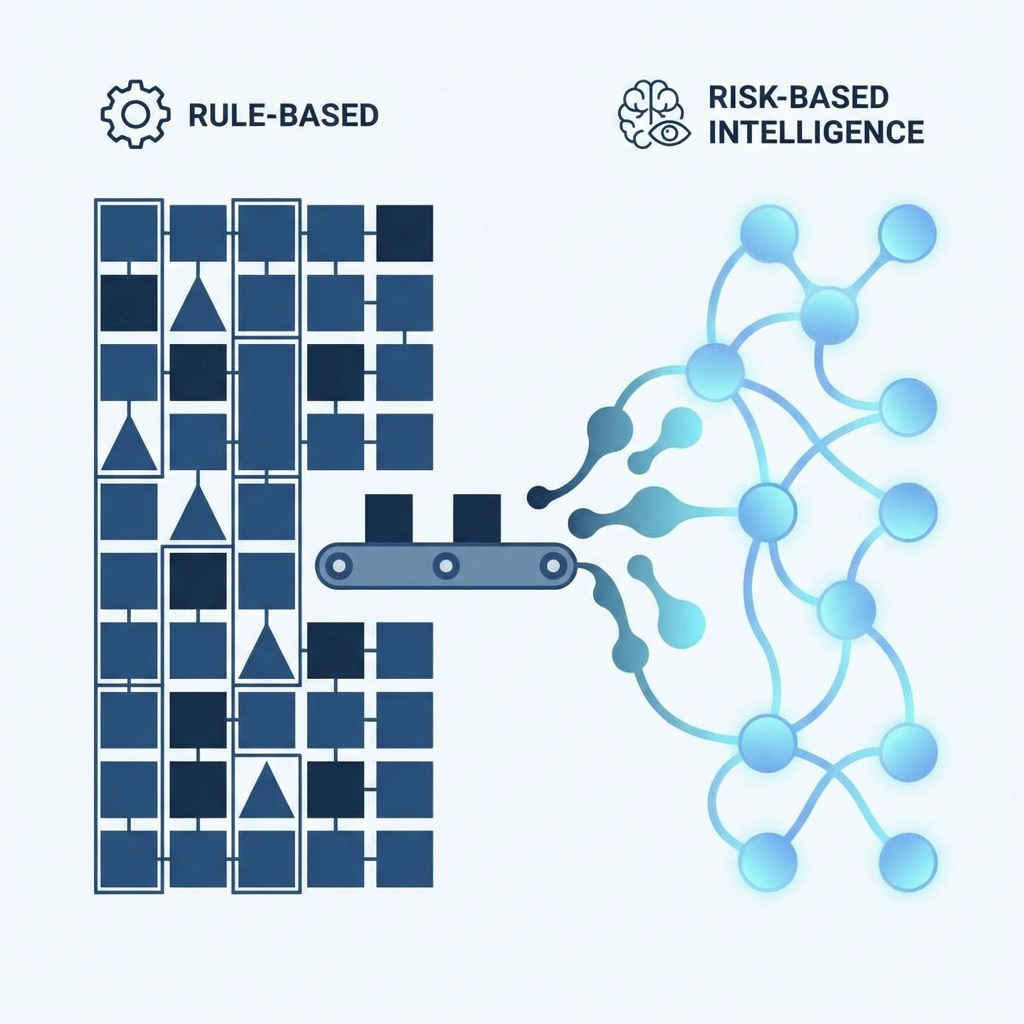
Step 1: Abandon Rule-Based Systems for Risk-Based Intelligence
Traditional AML systems rely on rigid rule sets that treat all transactions equally. A wire transfer above $10,000 triggers an alert, regardless of whether it comes from a verified customer making their monthly business payment or a suspicious entity with no transaction history.
Risk-based approaches revolutionize this paradigm by developing comprehensive profiles for monitored entities. Instead of applying blanket rules, these systems assess each transaction within its specific context: customer history, transaction patterns, geographic factors, and business relationships.
This transformation dramatically reduces false positive volumes while improving threat detection accuracy. When your system understands that a customer regularly makes large payments for inventory purchases, it won't flag their monthly supplier payments as suspicious. Conversely, it will immediately identify genuine anomalies when that same customer suddenly starts sending small, frequent transfers to high-risk jurisdictions.
The implementation requires recalibrating your entire monitoring framework, but the results justify the effort. Organizations implementing risk-based approaches report 60-80% reductions in false positive alerts while maintaining or improving their ability to detect genuine suspicious activity.
Step 2: Transform Your Data Quality Foundation
AML systems depend entirely on accurate, complete, and current data. When information is fragmented, outdated, or incomplete, false positives multiply exponentially. A customer sharing a name with someone on sanctions lists, incomplete business ownership structures, or outdated address information all trigger unnecessary alerts.
Data quality improvements require systematic investment in multiple areas. First, ensure all data sources receive regular updates. Sanctions lists, PEP databases, and adverse media sources change constantly: systems operating on monthly updates miss critical information that could eliminate false positives.
Second, implement comprehensive data validation at entry points. When customers provide information during onboarding, validate it immediately against authoritative sources. This prevents downstream complications when partially accurate information triggers monitoring systems.
Third, establish data enrichment protocols that supplement basic customer information with contextual intelligence. Understanding a customer's industry, typical transaction patterns, and business relationships enables more accurate risk assessment and reduces false positive generation.
Step 3: Integrate Comprehensive Screening at Onboarding Entry Points
Most institutions screen customers after they've already begun the onboarding process, creating unnecessary friction when issues arise. Early integration of screening capabilities transforms this dynamic by identifying legitimate risks immediately when customer relationships begin.
This proactive approach enables appropriate due diligence measures without creating multiple verification requests. When screening happens upfront, you can address genuine concerns through streamlined processes designed for efficiency rather than reactive investigations that disrupt customer experiences.

Early screening also enables dynamic risk scoring that adjusts throughout the onboarding process. As customers provide additional information and complete verification steps, their risk profiles become more accurate, reducing the likelihood of false positive alerts in subsequent screening stages.
Step 4: Deploy AI-Powered Pattern Recognition
Artificial intelligence transforms AML monitoring from reactive alert generation to proactive risk assessment. AI systems analyze complex patterns across multiple dimensions simultaneously: transaction amounts, frequencies, counterparties, geographic factors, and temporal patterns: to distinguish between legitimate high-value transactions and genuinely suspicious activity.
Machine learning algorithms continuously improve their accuracy by learning from historical false positive investigations. When compliance teams mark alerts as false positives, the system adjusts its parameters to avoid similar mistakes in the future. This creates a feedback loop that progressively reduces alert volumes while improving detection accuracy.
Advanced AI implementations incorporate natural language processing to analyze unstructured data sources, including adverse media and regulatory communications. This comprehensive analysis provides context that rigid rule-based systems cannot achieve, enabling more accurate risk assessments and fewer false positive alerts.
Step 5: Establish Continuous Calibration and Performance Monitoring
Effective false positive reduction requires ongoing system optimization based on real-world performance data. This means tracking false positive rates across different transaction types, customer segments, and monitoring parameters, then adjusting thresholds and rules based on empirical results.
Monthly calibration reviews should analyze alert volumes, investigation outcomes, and missed detection incidents to identify optimization opportunities. When specific rules or parameters generate excessive false positives without corresponding threat detection benefits, they require immediate adjustment.
Performance monitoring extends beyond technical metrics to include business impact measurements. Track customer abandonment rates, onboarding completion times, and compliance team productivity to understand how system changes affect operational outcomes. This comprehensive approach ensures that false positive reduction efforts improve both compliance effectiveness and business performance.
Implementation Success Requires Strategic Commitment
Reducing false positive rates demands coordinated effort across technology, compliance, and customer experience teams. The most successful implementations begin with executive commitment to balancing compliance effectiveness with operational efficiency.
Start by establishing baseline measurements for current false positive rates, customer onboarding completion times, and compliance team productivity. These metrics provide clear targets for improvement and enable objective assessment of implementation success.
Prioritize changes based on immediate impact potential. Data quality improvements and risk-based approach adoption typically deliver the fastest results, while AI implementation requires longer development timelines but provides sustained long-term benefits.
The financial services landscape rewards institutions that successfully minimize false positives while maintaining security. Organizations that eliminate unnecessary friction from customer onboarding while preserving robust compliance capabilities capture and retain more customers in increasingly competitive markets.
Your compliance team's expertise becomes a strategic advantage when freed from investigating obvious false positives. Instead of wasting resources on routine transactions that clearly pose no risk, they can focus on sophisticated threat detection and strategic compliance initiatives that protect your institution and serve your customers effectively.